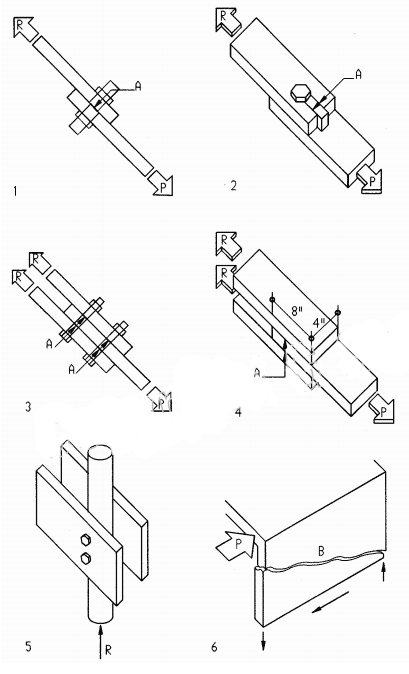
Shear stress occurs in many situations, including the following examples, but also in conjunction with bending, described in the next chapter on bending. Shear stress develops as a resistance to sliding of adjacent parts or fibers, as shown on the following examples. Depending on the number of shear planes (the joining surface [A] of connected elements) shear is defined as single shear or double shear.
A Shear plane
B Shear crack
A Shear plane
B Shear crack